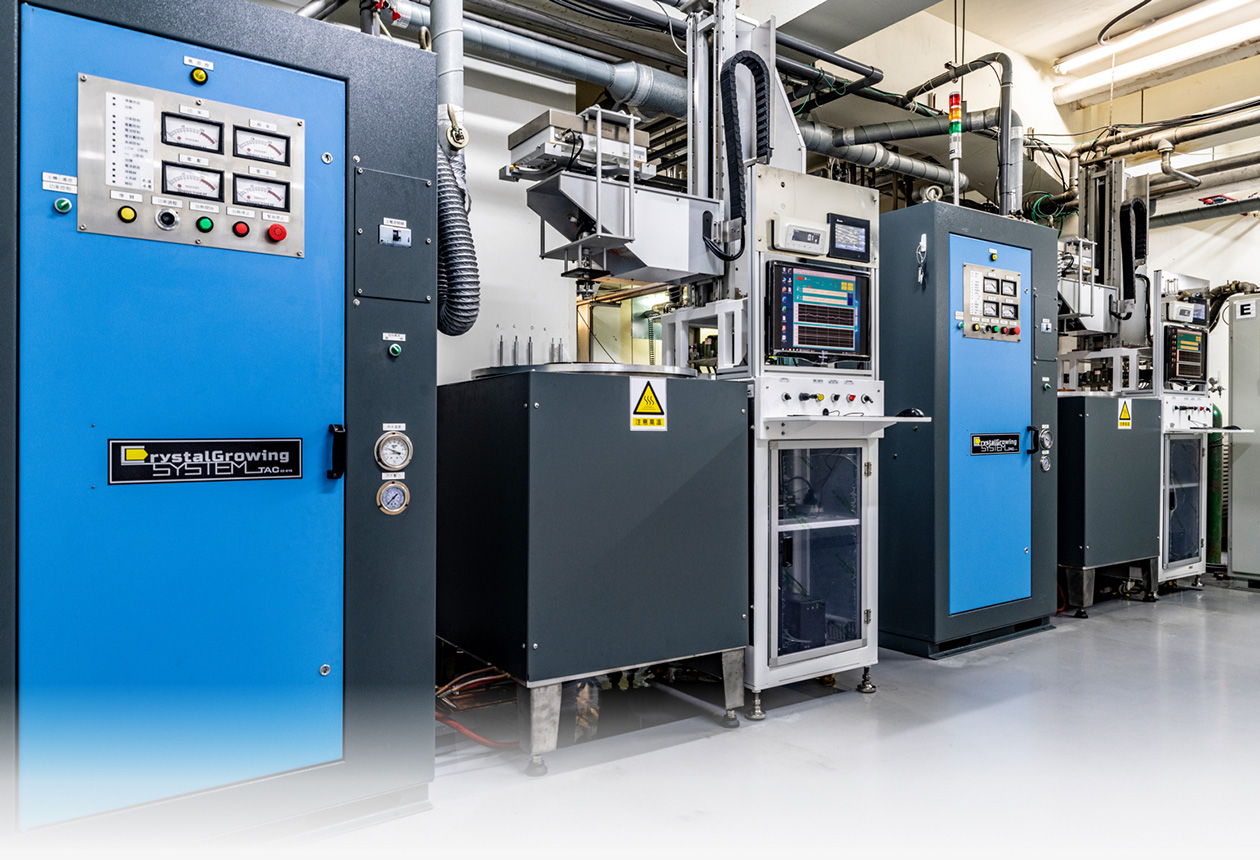
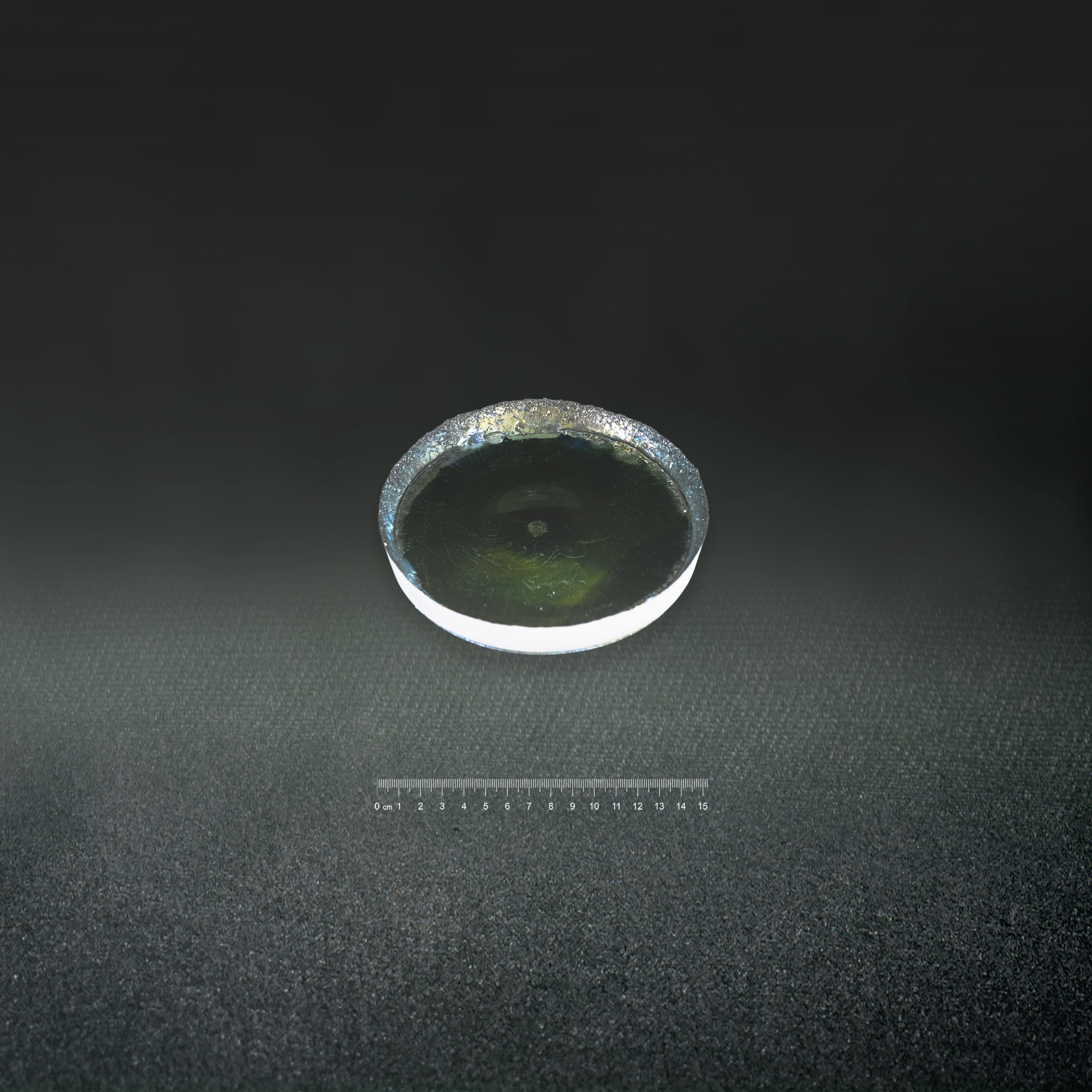
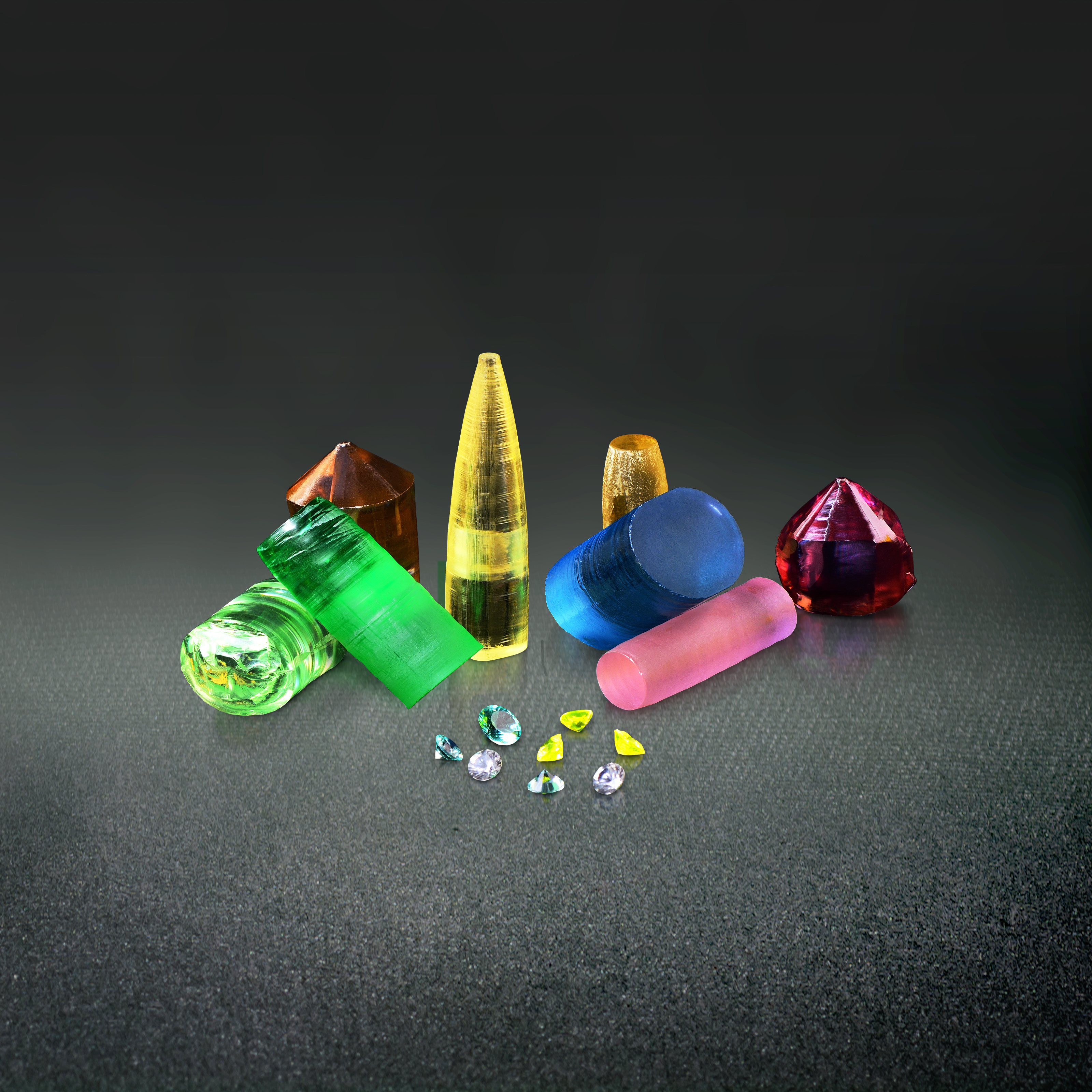
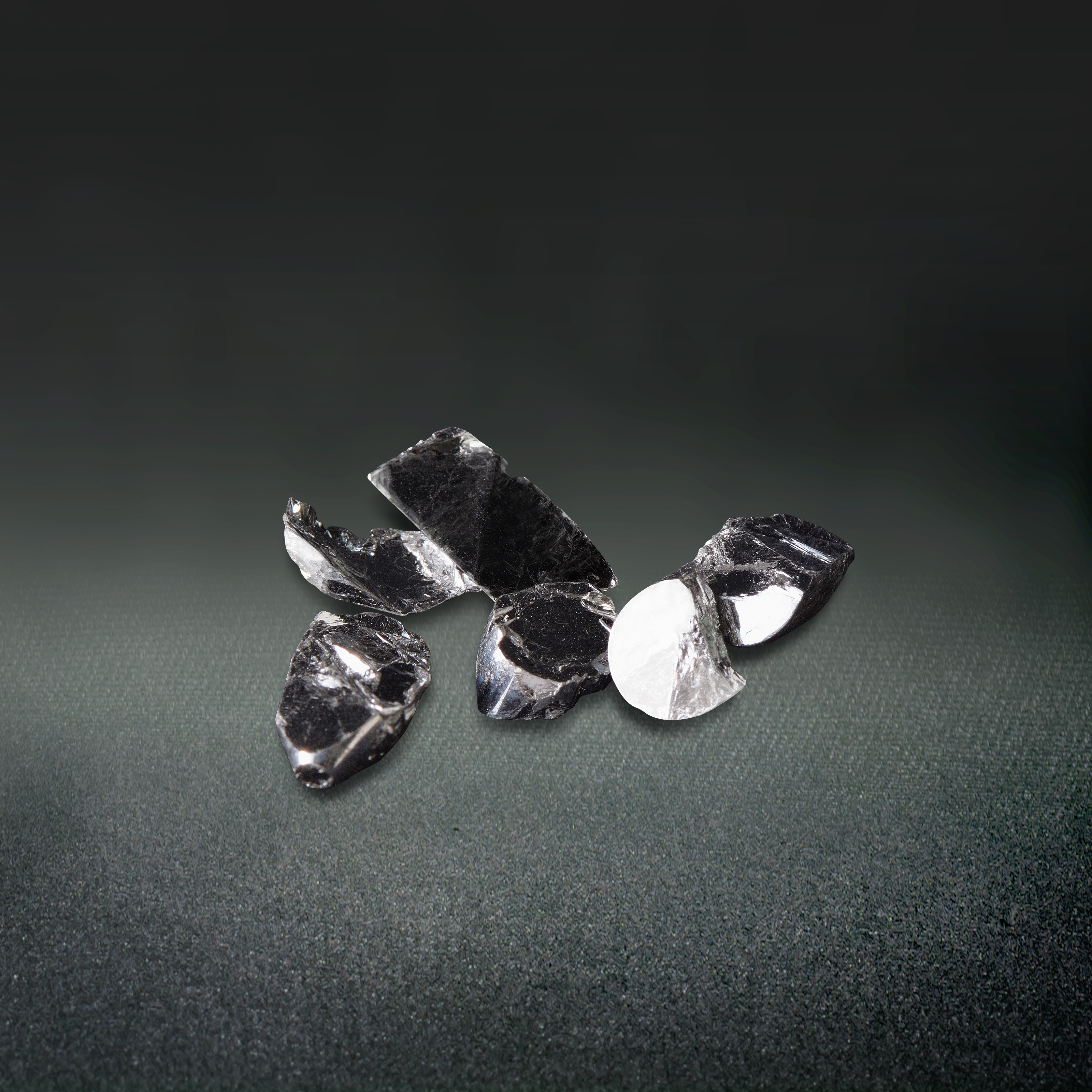
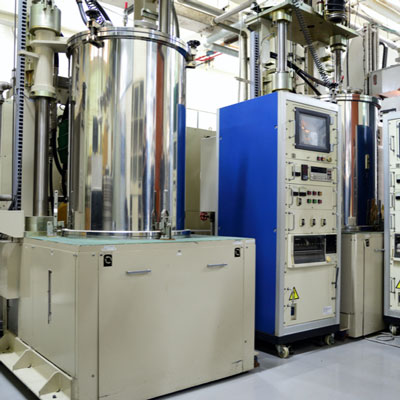
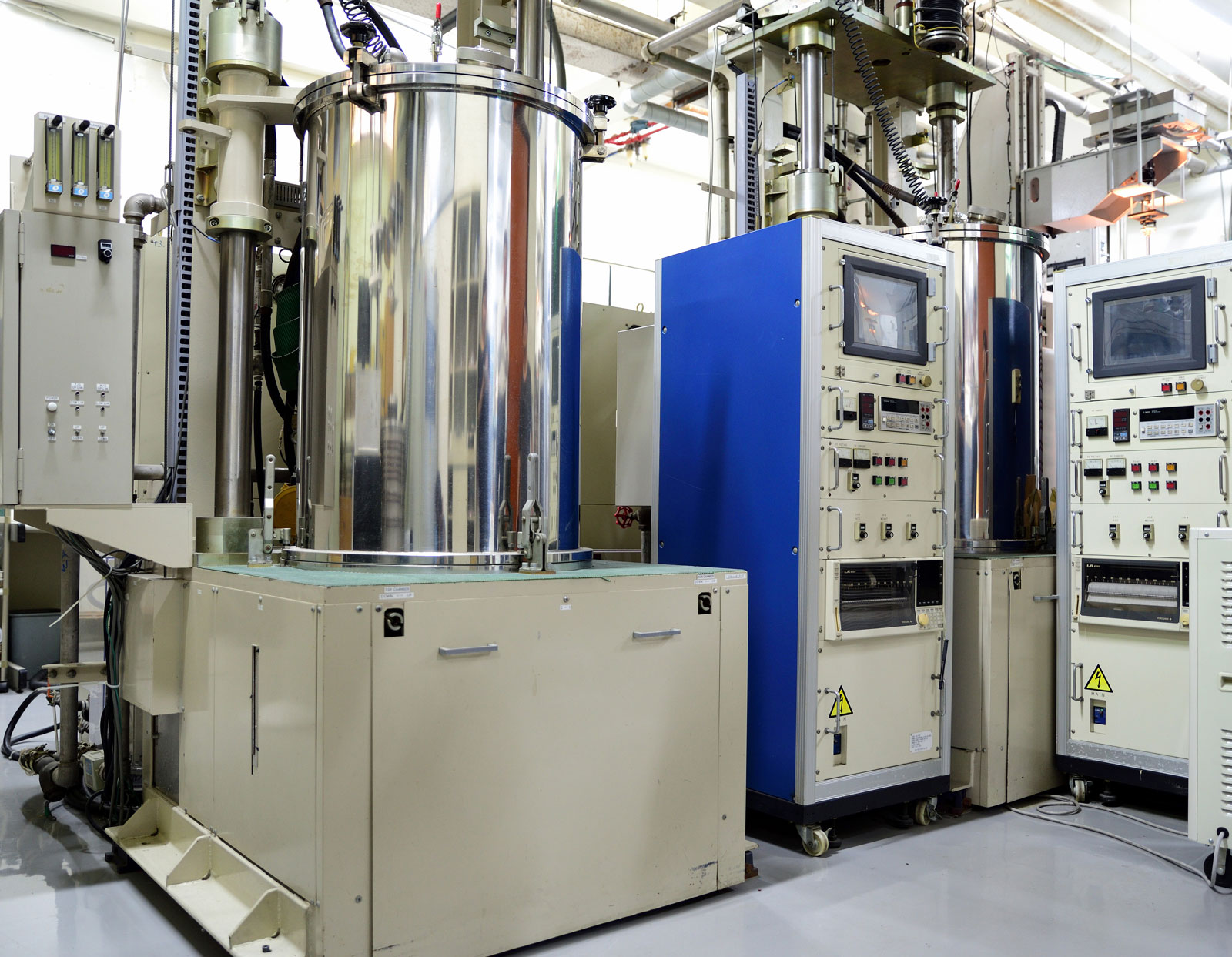
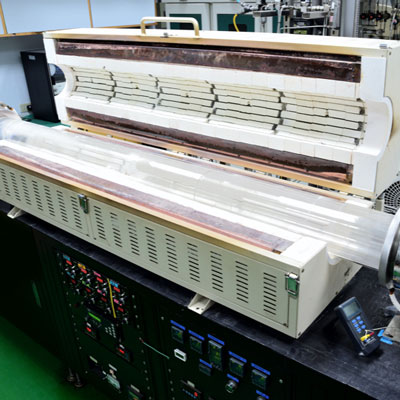
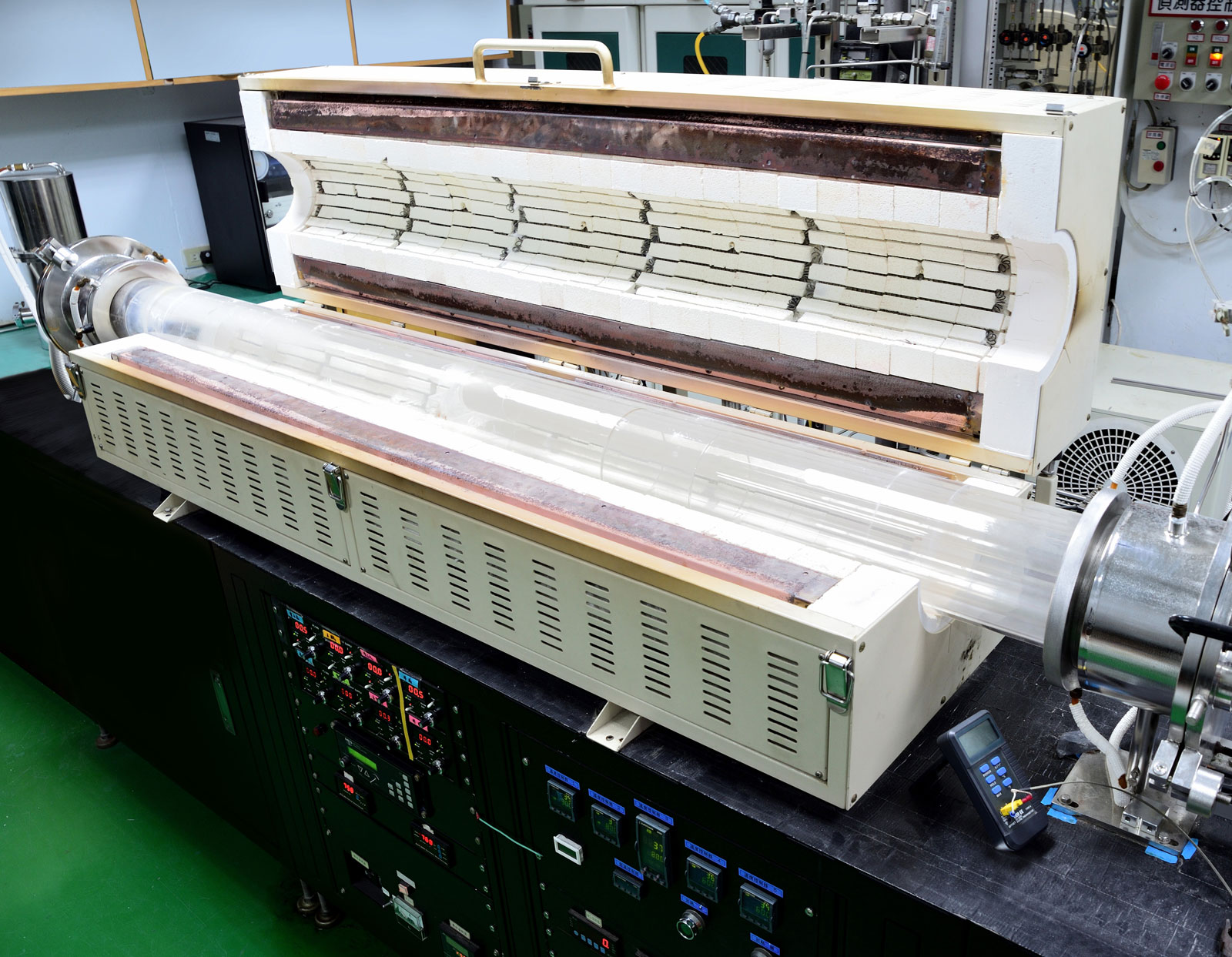
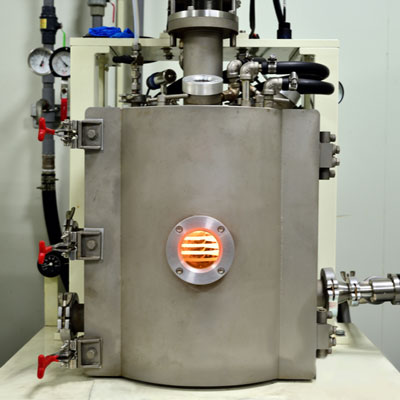
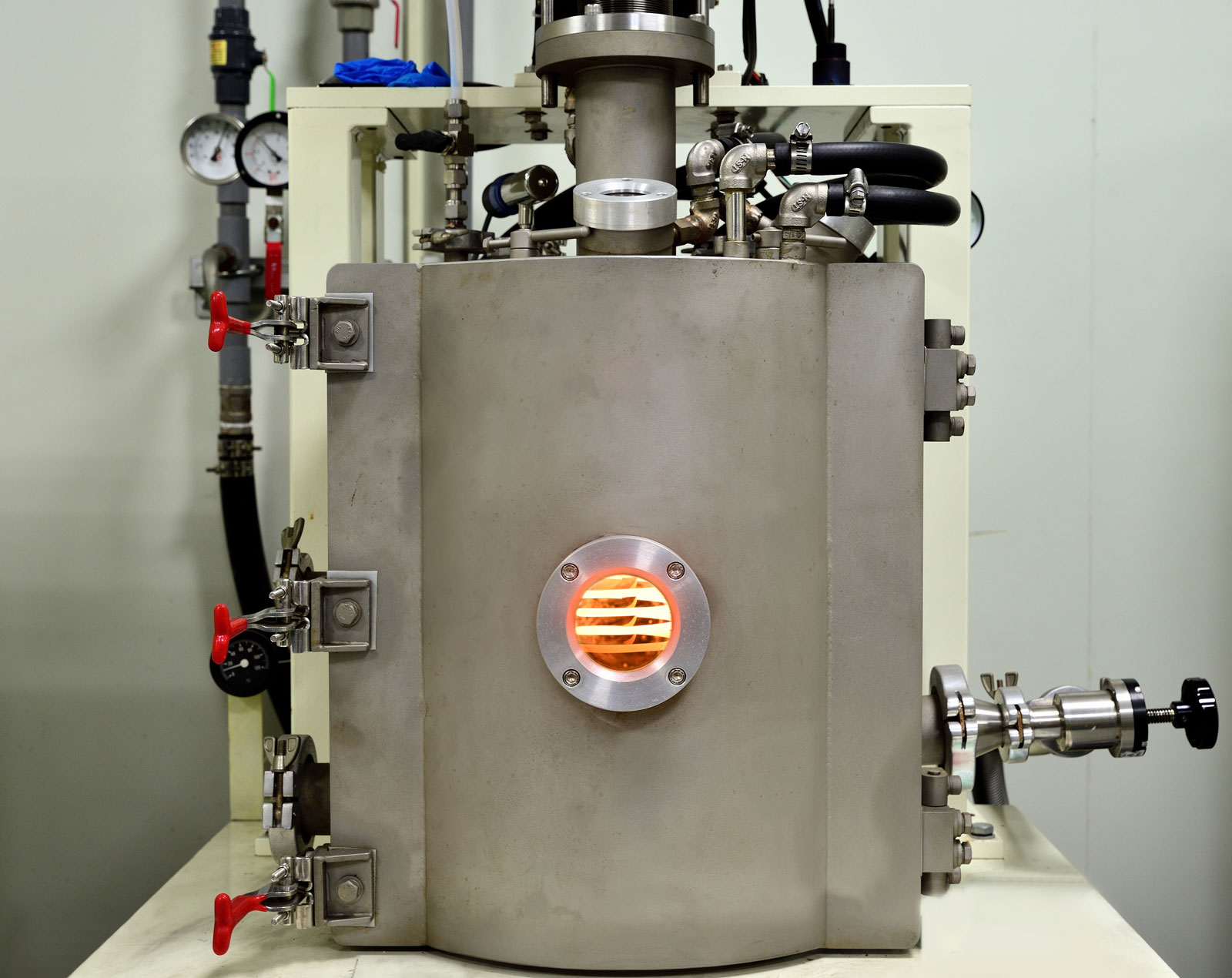
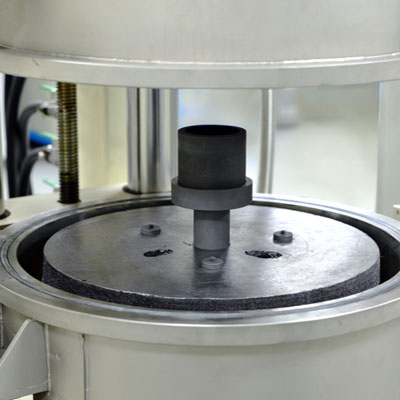
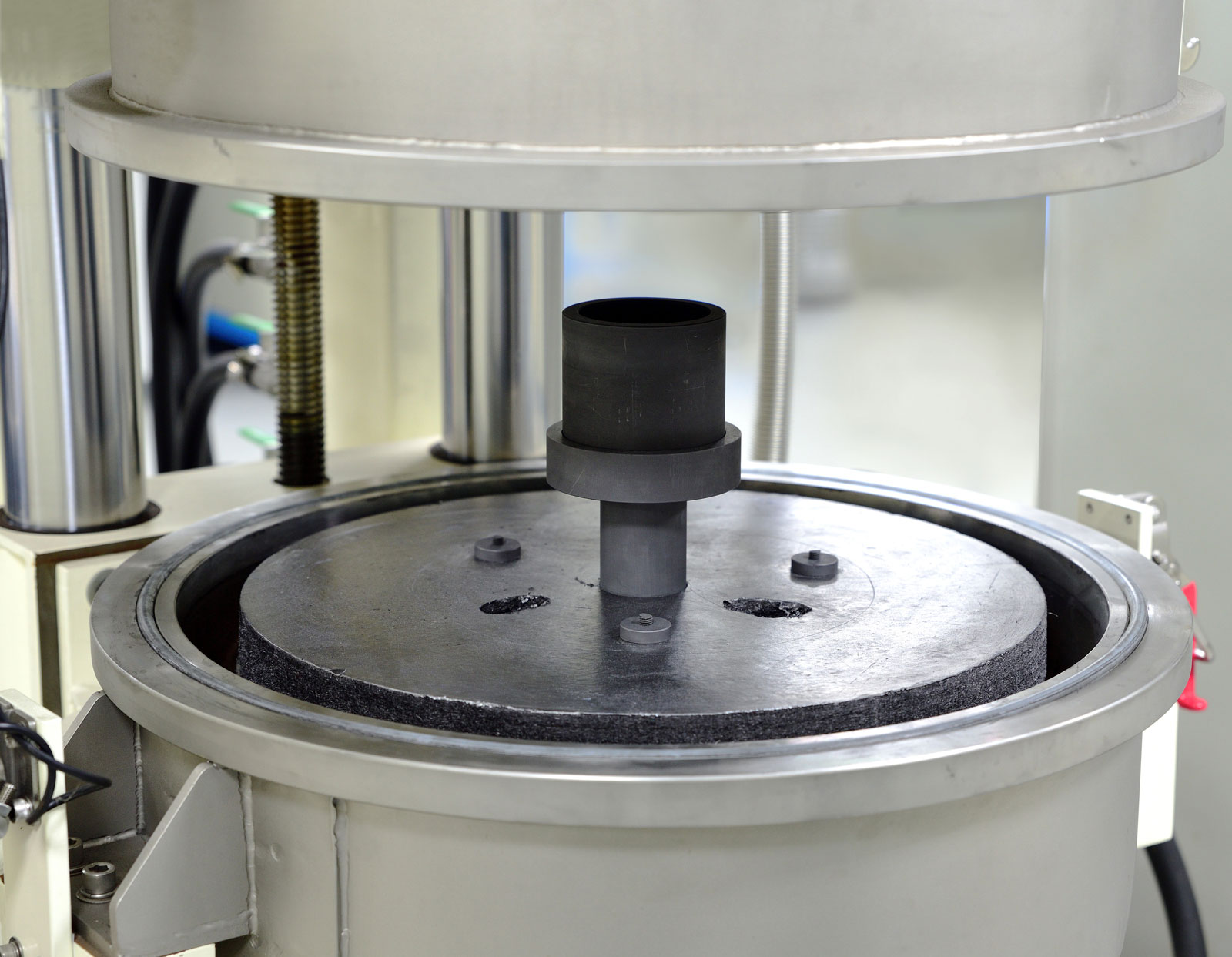
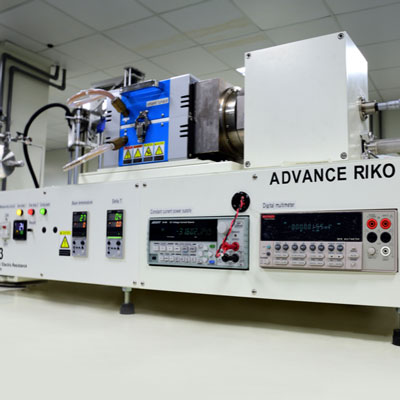
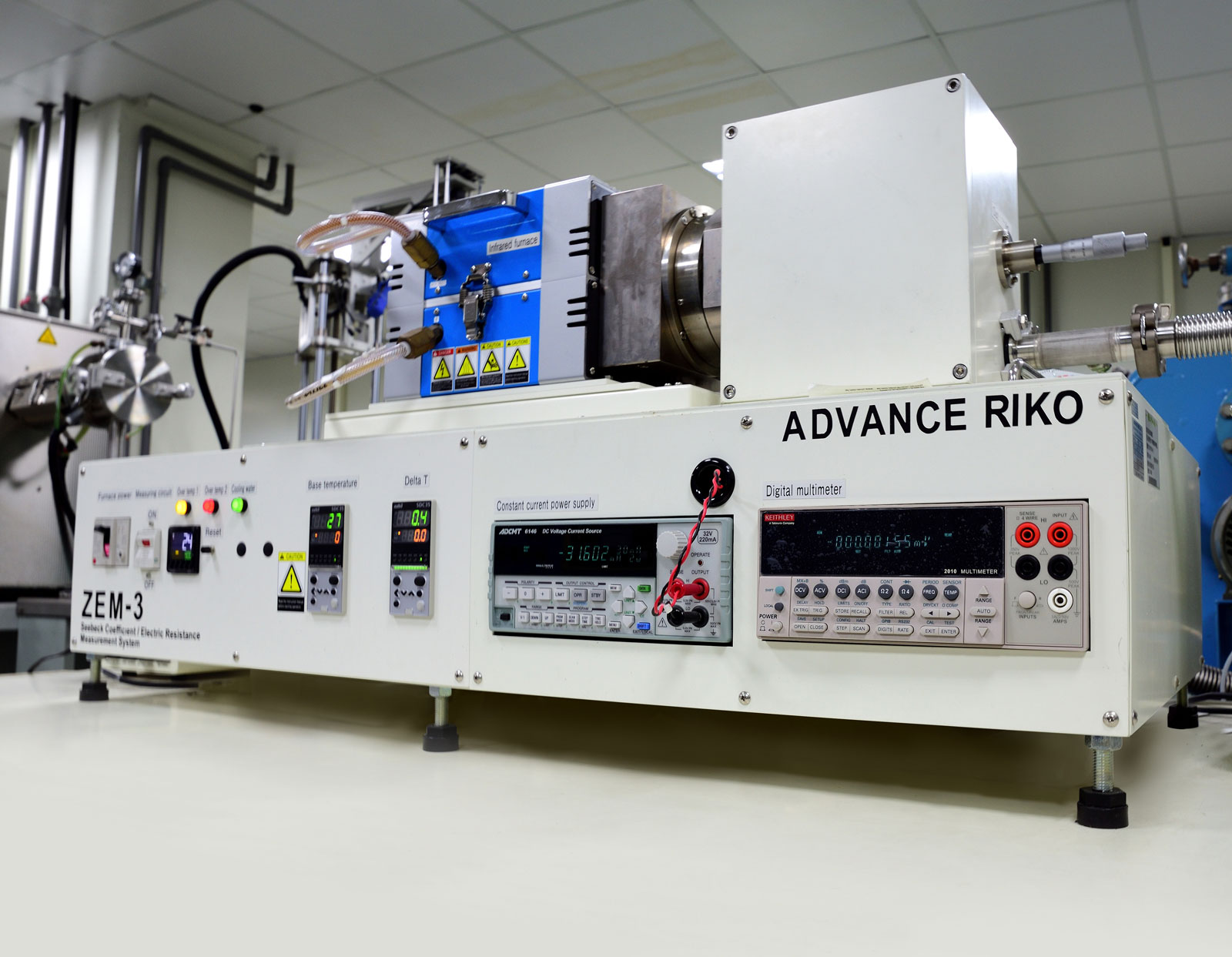
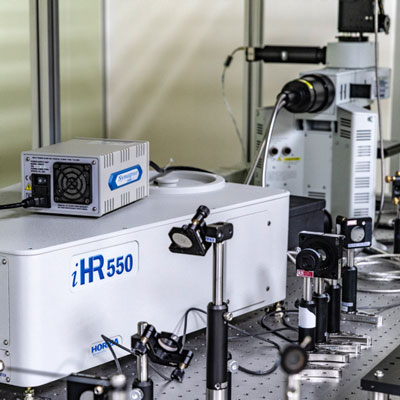
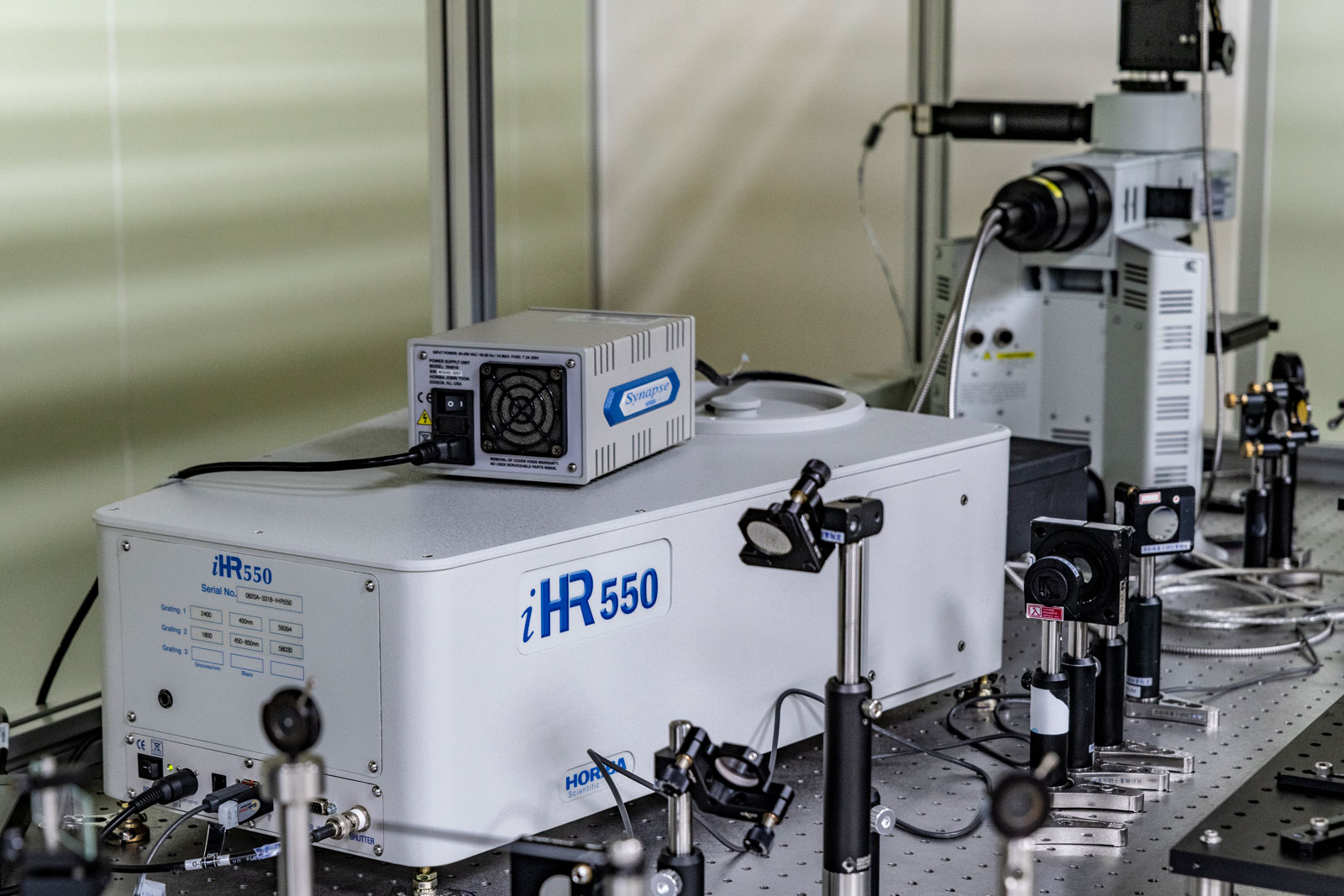
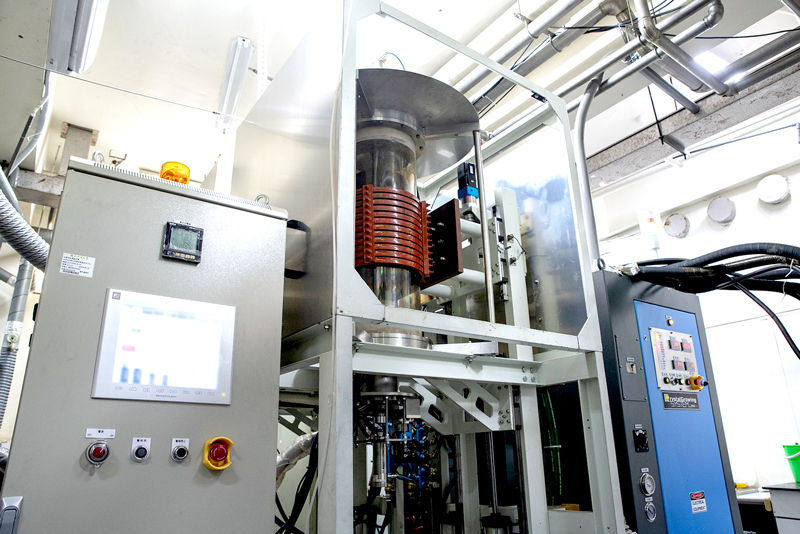
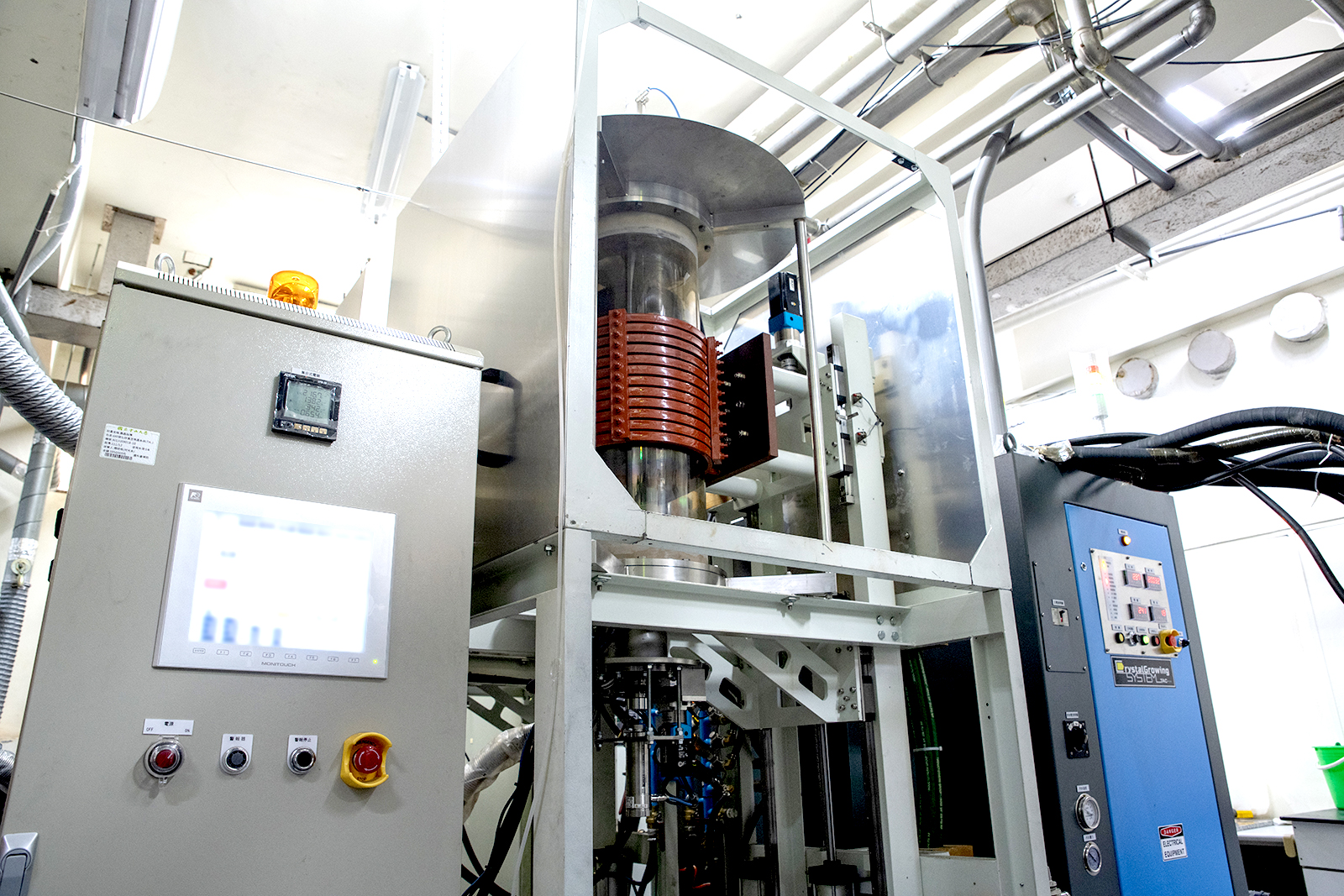
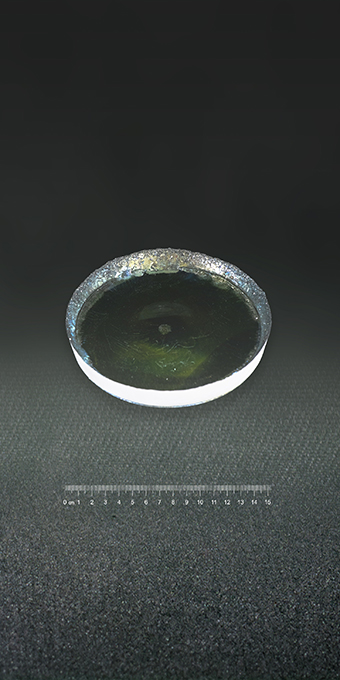
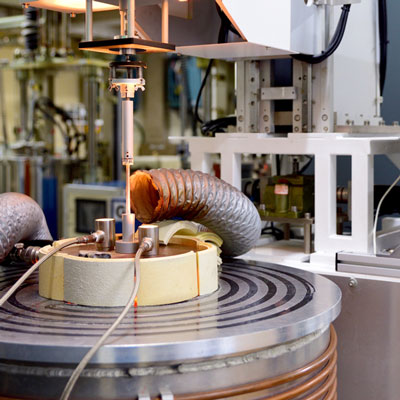
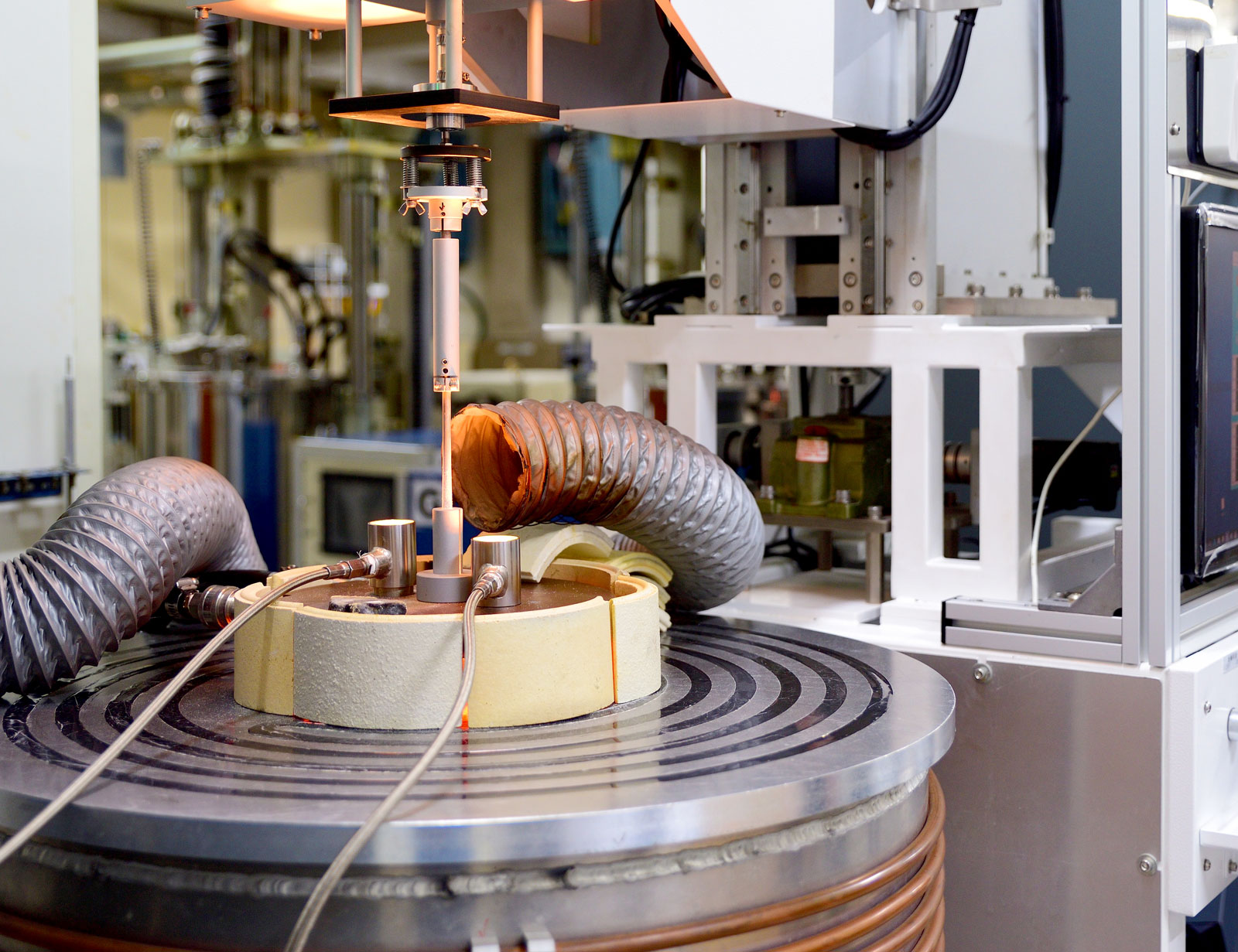
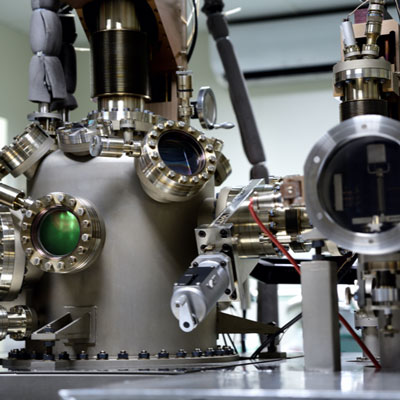
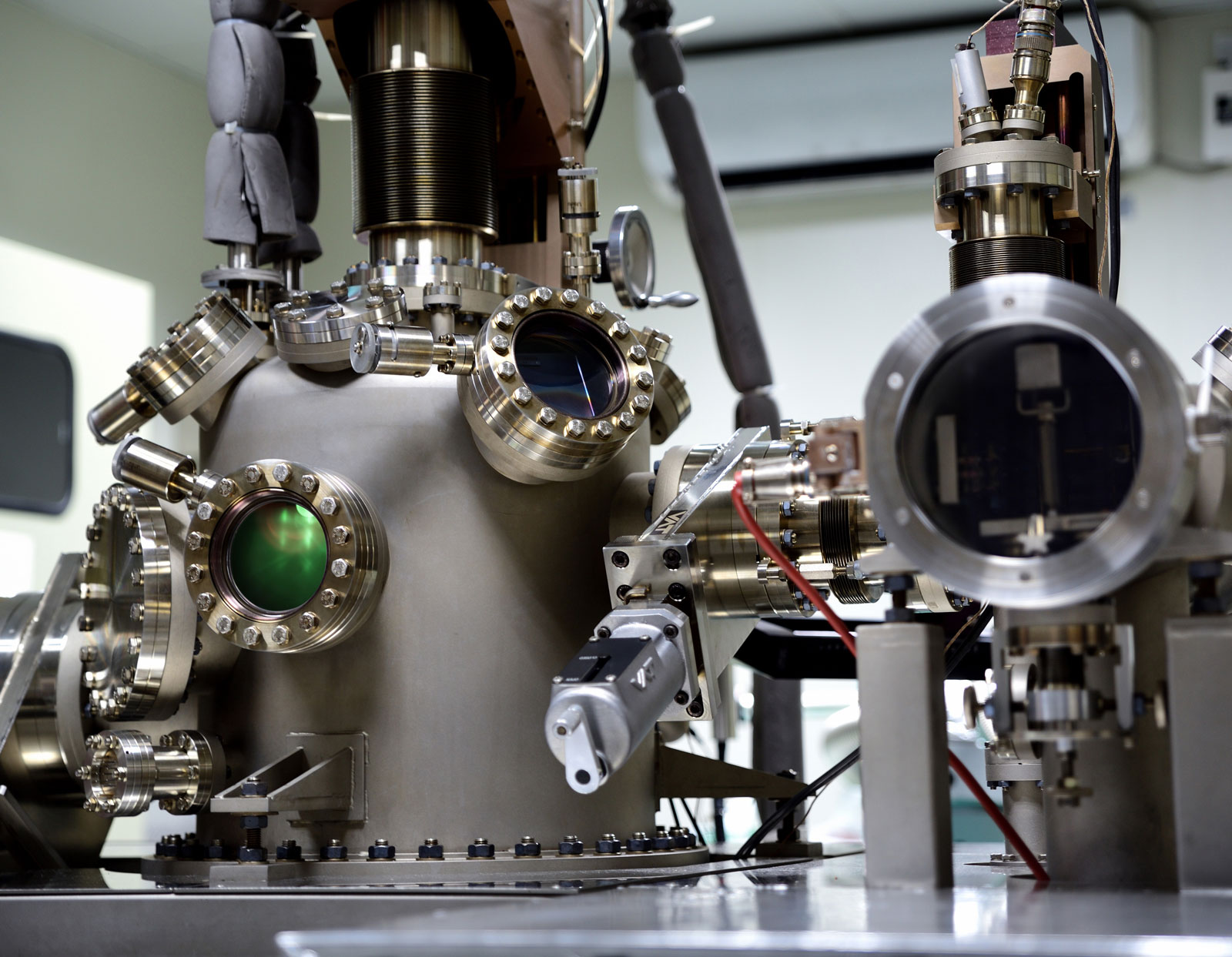
Crystalline material is one of the national tactical resources, and the growth of crystals is an important way to explore novel materials. Growing single crystals is a time-consuming process and there is no simple turn-key solution.
Crystalline materials are classified into two main categories:
- Crystals for condensed matter physics, including high temperature superconductor, magnetic crystals, skyrmion, heavy fermion and topological insulator.
- Crystals for laser, nonlinear optics, semiconductor, piezoelectric material, compound semiconductor, oxide substrate, medical image and high energy physics.
This Center has the capacity to grow crystals in both categories. Furthermore, we also have the knowledge and experience to design crystal growth furnaces for different applications.
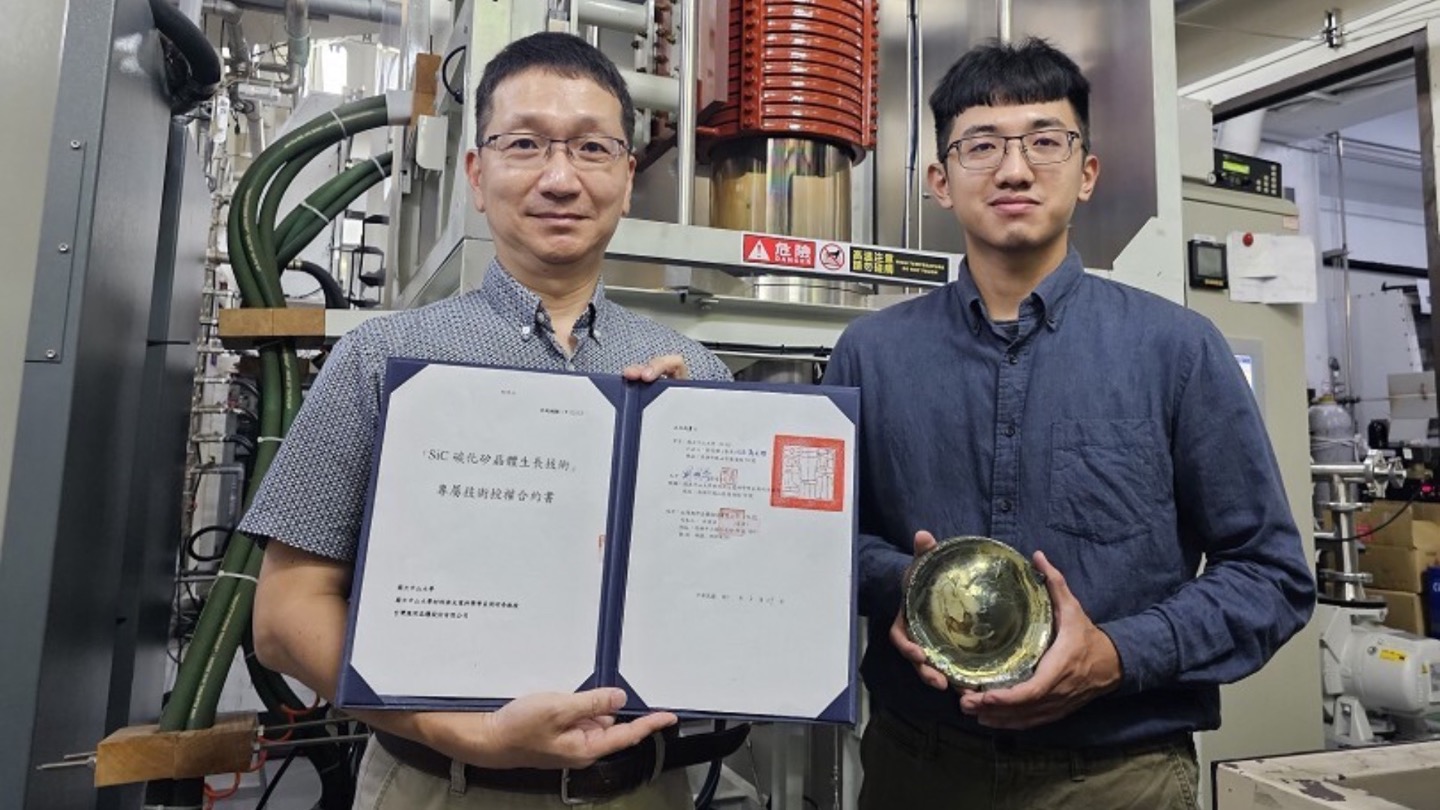
The research team is led by Chair Professor Mitch M.C. Chou from Academy of Innovative Semiconductor and Sustainable Manufacturing at NCKU. Dr. Chou has extensive experience in the field of crystal growth science and he received the “Award for Outstanding Contributions in Science and Technology” from the Executive Yuan of Taiwan in 2014.